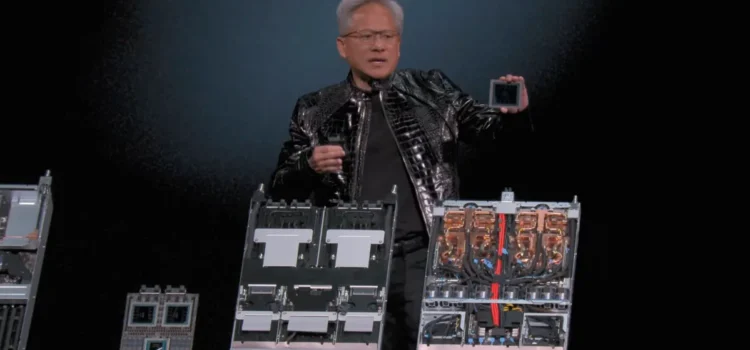
At CES 2026, NVIDIA introduced the Rubin platform, and Intel announced the Xeon 600 series (Granite Rapids WS). These two products take different but complementary paths to improve data center AI efficiency. Rubin targets large-scale, high-intensity AI training and inference with up to 10x lower cost per token. In contrast, the Intel Xeon 600 series is built for flexible, high-core-count CPU-based AI and workstation tasks.
NVIDIA Rubin Platform Efficiency Through Extreme Scale (2026)
The Rubin platform, which follows Blackwell, is built for agentic AI and large transformer models. It aims to get the most performance per watt, so fewer large GPU arrays are needed.
Key Efficiency Metrics (vs. Blackwell):
- Inference Costs cut the cost per token by up to 10x for mixture-of-experts (MOE) models.
- Training speed: Needs 4x fewer GPUs to train large AI models than Blackwell.
- System power: The Vera Rubin NVL72 rack uses about 120-130 kW, like current systems, but delivers much higher performance.
Architecture Innovations:
- Rubin GPU: features 336 billion transistors, 50 petaflops of NVFP4 compute, and 128 GB of GDDR7 memory.
- Vera CPU: has 66 ARM cores and built-in NVLink C2C for fast, direct GPU connections, which boosts system-wide energy efficiency.
- Networking includes 6th-generation NVLink at 3.6 TB/s per GPU and Spectrum-X Ethernet photonics, which is 5x more powerful and power-efficient.
Target workload: Intended for large-scale training and real-time inference with long contexts, such as video or complex thinking tasks.
Intel Xeon 600 Series: Efficiency Via Specialized Compute (2026)
The Intel Xeon 600 series, especially Granite Rapids-WS, is made for high-performance workstations and data center nodes that need flexible, high-speed processing.
Key efficiency metrics (vs. prior generation):
- AI performance: delivers up to 17% faster AI and machine learning workloads thanks to Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) and FB16 support.
- Multi-threading: Offers up to 61% better performance, speeding up preprocessing and model fine-tuning.
- Memory bandwidth: Supports DDR5 MRDI MMS at 8000 MT/s, which is important for memory-heavy AI workloads.
Architecture Innovations:
- Core count provides up to 86 performance cores (Redwood Cove+).
- Connectivity: Offers 128 lanes of PCLE, Gen 5.0, and CXL 2.0, supporting dense multi-GPU setups.
Target workload: Suited for AI preprocessing, inference on smaller, fine-tuned models, and high-performance computing that needs flexible CPU and GPU scaling instead of only GPU scaling.
Direct Comparison for 2026 AI Workloads
| Feature. | NVIDIA Rubin platform (2026) | Intel Xeon 600 (Granite Rapids-WS) |
| Primary goal. | Max AI performance per watt (scale) | Flexible/ Balanced Compute Density |
| AI Focus | Large-scale LLM/Agentic training/inference. | AI, preprocessing, fine-tuning, and inference. |
| Key Advantage | ~10x lower token cost vs Blackwell. | High-speed DDR5, 86 core efficiency. |
| GPU/CPU link | NVL6 (3.6 TB/s) | PCLE Gen 5.0 (128 Lanes) |
| Memory | HBM4 up to 288 (up to 288 per GPU.) | DDR5/MRDIMM up to 8 TB+ capacity. |
| Performance | ~50PFLOPS/NVFP4 | 17% faster AI via AMX (vs prev) |
Conclusion on Efficiency:
- NVIDIA Rubin is the best option for large-scale AI training and inference with 1 million token contexts, delivering the highest performance per token.
- The Intel Xeon 600 series offers greater efficiency for data-intensive workloads, preprocessing, and scenarios that require flexible scaling within a two-socket server with superior memory bandwidth for non-GPU-bound tasks.
NVIDIA has launched the NVIDIA Rubin Platform, which includes six new chips that work together to create a powerful AI supercomputer. Rubin is designed to make it easier and more affordable to build, deploy, and secure advanced AI systems, helping more people use AI in their work.
The Rubin platform brings together 6 chips:
- NVIDIA Verus CPU
- Rubin GPU
- NVLink 6 switch
- ConnectX 9 SuperNIC
- Bluefield-4 DPU
- Spectrum-6 Ethernet switch
These chips are designed to work closely together. This solution helps reduce both training time and the cost of running AI models.
The NVIDIA Rubin GPU uses a third-generation transformer engine and hardware-accelerated adaptive compression. It provides 50 petaflops of NVFP4 compute power for AI inference.
Vera Rubin NVL72 is the first rack-scale platform to offer third-generation NVIDIA confidential computing. This technology keeps data secure across GPU, CPU, and NV Link domains, protecting both large proprietary models and training and inference workloads.
The Rubin platform, which includes GPUs, CPUs, and NV Link, features a second-generation RAS engine for instant health checks, fault tolerance, and pre-emptive maintenance to boost system performance. Its modularized, cable-free tray design enables assembly and servicing up to 18x faster than Blackwell.